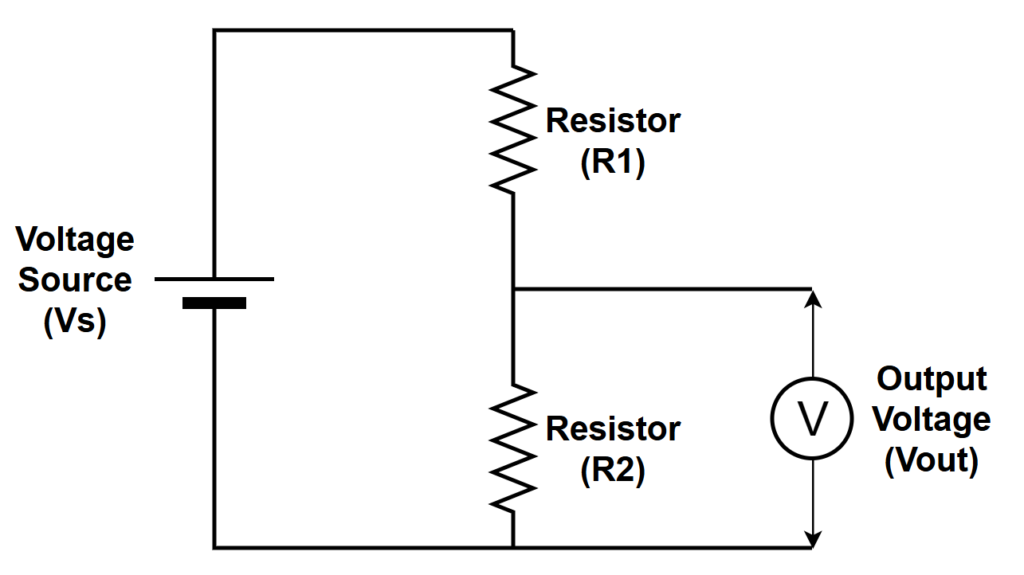
Voltage Divider Calculator (Bidirectional)
Solve any one of Vin, Vout, R1, R2 from the other three. R1 is the top resistor (to Vin), R2 is the bottom resistor (to ground).
Values
Solve For
Core relation: Vout = Vin · R2 / (R1 + R2). R1,R2 > 0, and for passive divider Vout ∈ (0, Vin).
Results
Vin
—
Vout
—
R1
—
R2
—
Divider Current & Power
Idiv
—
PR1
—
PR2
—
Total Pin
—
Equations Used
—
How to Use the Voltage Divider Calculator
Design and analyze a divider in both directions. Compute Vout from Vin, R1, R2, solve missing resistor from a target Vout, include a load RL, or design R1/R2 from a target divider current.
1) Choose a mode
- Vin, R1, R2 → Vout (no-load / with RL)
- Vin, Vout, R1 → R2 (no-load or with RL)
- Vin, Vout, R2 → R1 (no-load or with RL)
- Vin, Vout, Idiv → R1 & R2 (design mode, no-load)
“Loaded” modes use the effective bottom branch Req = R2 ∥ RL.
2) Enter the inputs
- Type Vin, any known resistors (R1/R2), optional RL, or target Idiv.
- Leave unknowns blank—the calculator solves them and highlights computed boxes.
- Resistances must be ≥ 0. Use realistic ranges (Ω, kΩ, MΩ).
3) Set units & polarity
- Voltage: V/mV/kV • Resistance: Ω/kΩ/MΩ • Current (design): A/mA.
- Signs: Vin/Vout may be ± (for reference polarity). Resistances stay non-negative.
4) Read the outputs
- Vout (no-load), Vout (with RL), Idiv (no-load), Rth, and per-resistor power.
- The details table shows branch currents and the exact formulas used.
Quick Examples
Compute Vout (no-load)
Given: Vin = 12 V, R1 = 18 kΩ, R2 = 12 kΩ
Vout = Vin · R2 / (R1 + R2)
= 12 · 12k / 30k = 4.8 V
I_div = Vin / (R1 + R2) = 0.4 mASolve R2 from Vin, Vout, R1 (no-load)
Given: Vin = 5 V, Vout = 1.8 V, R1 = 10 kΩ
R2 = (Vout · R1) / (Vin − Vout)
= 1.8 · 10k / 3.2 = 5.625 kΩLoaded divider: find R2 with RL
Given: Vin = 12 V, Vout = 3.3 V, R1 = 22 kΩ, RL = 10 kΩ
Let X = R2 ∥ RL = (k · R1)/(1 − k), where k = Vout/Vin = 0.275
X = 0.275 · 22k / 0.725 ≈ 8.34 kΩ
R2 = (X · RL) / (RL − X) ≈ (8.34k · 10k) / (1.66k) ≈ 50.2 kΩDesign R1 & R2 from Idiv (no-load)
Given: Vin = 24 V, Vout = 2.5 V, I_div = 0.5 mA
R_total = Vin / I_div = 48 kΩ
k = Vout/Vin = 0.1042 → R2 = k·R_total = 5.0 kΩ, R1 = 43.0 kΩ