Cuk Converter Designer
Professional design tool for Cuk Converters. This topology provides Low Output Ripple and inverting capability (Negative Output), making it superior to standard Buck-Boost for sensitive analog circuits.
Specs & Margins
Input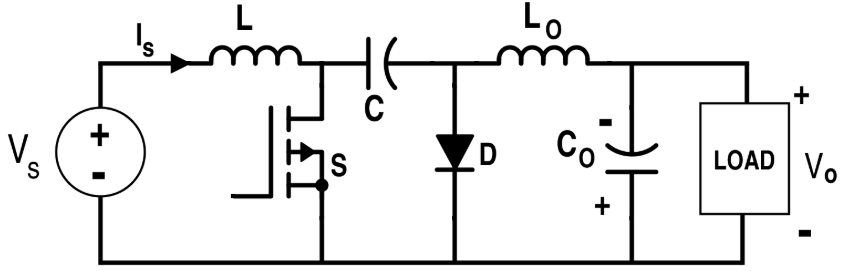
Design Analysis
CCM ModeCuk Converter vs Buck-Boost
Why choose the more complex Cuk topology over a standard Buck-Boost?
| Feature | Cuk Converter | Buck-Boost (Inv) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Current | Continuous (Low Ripple) | Pulsed (High Noise) |
| Output Current | Continuous (Low Ripple) | Pulsed (High Noise) |
| Energy Transfer | Capacitive (C1) | Inductive (L) |
| Use Case | Low-Noise Audio / RF | General Purpose |
Physics Explained
Capacitive Energy Transfer
Unlike other converters that use an inductor, the Cuk uses a central capacitor (C1) to transfer energy. This component handles high RMS current and must be a high-quality film or ceramic type.
Continuous Current
Both input (L1) and output (L2) inductors ensure that current flow is continuous. This results in significantly lower EMI and output voltage ripple compared to Buck-Boost.
Inverting Output
Like the Buck-Boost, the Cuk converter inverts the voltage polarity. A positive input produces a negative output.
How to Use
Set Voltages
Define Vin and the absolute value of Vout. The calculator assumes CCM operation for low ripple design.
Size Coupling Cap
Pay close attention to the Coupling C1 IRMS. This capacitor is the heart of the converter and undergoes significant stress.
Check Inductors
The tool calculates separate values for L1 (Input) and L2 (Output) to meet your ripple targets.
